Exploring the Differences Between SOXX and SMH in Semiconductor Trading
The world of semiconductor trading is a complex and ever-evolving one, with new developments and technologies constantly shaking up the market. Two popular exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that focus on this sector are the iShares PHLX Semiconductor ETF (SOXX) and the VanEck Vectors Semiconductor ETF (SMH). While both ETFs track semiconductor stocks, there are key differences between them that traders need to be aware of when deciding where to invest their money.
1. Index Composition:
One of the main differences between SOXX and SMH lies in their index composition. SOXX tracks the PHLX SOX Semiconductor Sector Index, which includes companies that are primarily involved in the design, distribution, manufacture, and sale of semiconductors. On the other hand, SMH tracks the MVIS US Listed Semiconductor 25 Index, which is composed of 25 of the largest semiconductor companies listed in the United States.
2. Weighting Methodology:
Another crucial difference between SOXX and SMH is their weighting methodology. SOXX follows a modified equal-weighting approach, where each stock in the index holds roughly the same weight. In contrast, SMH uses a market-cap weighting methodology, which means that companies with larger market capitalizations have a greater influence on the fund’s performance.
3. Performance and Volatility:
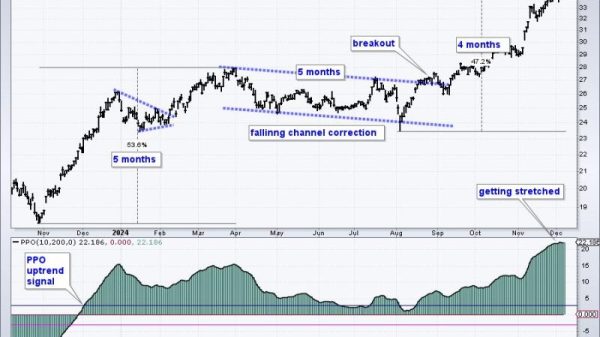
Due to their differing index compositions and weighting methodologies, SOXX and SMH may exhibit varying performance and volatility levels. For example, SOXX’s equal-weighting approach may lead to more balanced returns across its constituent stocks, potentially reducing volatility compared to SMH, which is more heavily influenced by larger companies with higher market capitalizations.
4. Industry Exposure:
While both ETFs focus on semiconductor stocks, they may offer slightly different industry exposure. SOXX’s index includes companies involved in various aspects of the semiconductor sector, from design to distribution, providing investors with a diversified exposure to the industry. In contrast, SMH’s index focuses on the 25 largest semiconductor companies, potentially offering a more concentrated exposure to market leaders.
In conclusion, while both SOXX and SMH offer investors exposure to the semiconductor sector, they have distinct differences in their index composition, weighting methodology, performance, volatility, and industry exposure. Traders looking to invest in this sector should carefully consider these factors and choose the ETF that aligns with their investment goals and risk tolerance. By understanding the nuances between SOXX and SMH, investors can make informed decisions to optimize their semiconductor trading strategy.