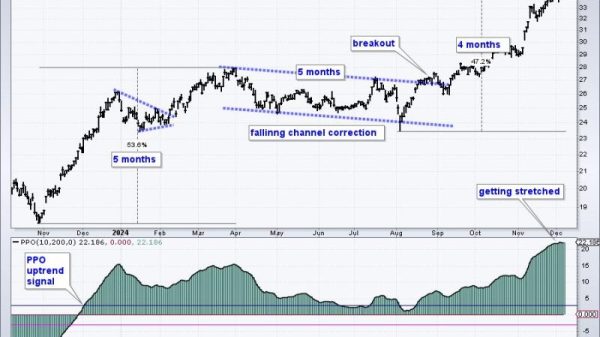
The recent report from the Federal Reserve indicating a 2.8% increase in the key inflation measure from a year ago in March has raised concerns among policymakers and economists alike. This uptick in inflation, which surpassed expectations, has fueled discussions about its implications for the economy and potential future policy responses.
One of the primary concerns stemming from the inflation surge is its impact on consumer purchasing power. As prices rise, consumers may find it more challenging to afford goods and services, ultimately affecting their overall spending habits. This decrease in purchasing power could lead to a slowdown in consumer spending, which is a significant driver of economic growth.
Furthermore, the rise in inflation could also have repercussions for businesses. Companies may face higher production costs as input prices increase, potentially squeezing profit margins. This scenario could prompt businesses to pass on these additional costs to consumers through price hikes, creating a cyclical effect that further fuels inflationary pressures.
The Federal Reserve closely monitors inflation data to guide its monetary policy decisions. The latest inflation figures may prompt the Fed to consider tightening monetary policy to curb rising prices and prevent the economy from overheating. This could involve raising interest rates or implementing other measures to reduce excess liquidity in the financial system.
Another factor to consider is the impact of inflation on the bond market. As inflation rises, bond investors become concerned about eroding real returns on their investments. This can lead to increased selling pressure on bonds, causing bond prices to fall and yields to rise. The resulting increase in interest rates can have far-reaching implications for borrowing costs and financial markets as a whole.
It is essential to consider the wider economic context in which inflation is rising. The ongoing recovery from the pandemic-induced recession could contribute to inflationary pressures as demand outstrips supply in certain sectors. Additionally, the recent fiscal stimulus measures and expansive monetary policy have injected significant liquidity into the economy, potentially fueling inflationary expectations.
In conclusion, the unexpected rise in the key Fed inflation measure underscores the complex interplay of factors shaping the economic landscape. Policymakers and market participants will need to closely monitor inflation trends and assess their implications for the broader economy. As the Federal Reserve navigates these challenges, striking the right balance between supporting economic growth and maintaining price stability will be crucial in shaping the path forward.