Moving averages are one of the most popular and effective technical analysis tools used by traders and investors in the financial markets. They are versatile indicators that can help in identifying trends, spotting potential reversals, and setting key entry and exit points for trades. In this article, we will delve deeper into five simple yet powerful uses for moving averages to enhance your trading strategy.
1. Trend Identification:
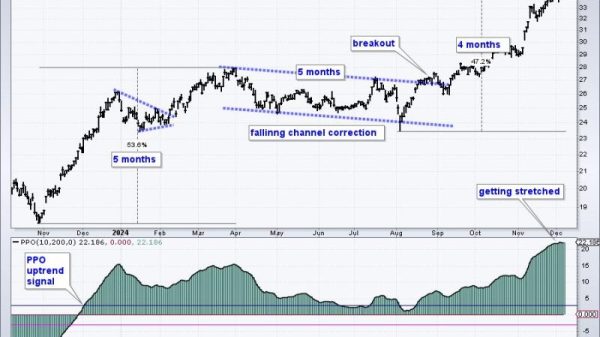
One of the primary uses of moving averages is to identify the direction of the underlying trend. By plotting a moving average on a price chart, traders can quickly visualize whether the market is trending up, down, or moving sideways. When the price is consistently above a rising moving average, it indicates an uptrend, whereas a price below a declining moving average suggests a downtrend. By observing the slope and positioning of different moving averages, traders can gain valuable insights into the overall market sentiment.
2. Support and Resistance Levels:
Moving averages can also act as dynamic support and resistance levels that help in determining potential price reversal points. For instance, the 50-day moving average is widely followed by traders and investors as a key support level during uptrends. If the price of an asset falls towards the 50-day moving average and bounces off it, it could signal a buying opportunity as the level is likely to provide a floor for the price. Conversely, in a downtrend, the 50-day moving average may act as a resistance level that prevents the price from moving higher.
3. Moving Average Crossovers:
One of the most common trading signals generated by moving averages is the crossover strategy. This strategy involves using two or more moving averages of different periods, such as the 50-day and 200-day moving averages, and looking for instances when they cross over each other. A bullish crossover occurs when a shorter-term moving average crosses above a longer-term moving average, signaling a potential uptrend. Conversely, a bearish crossover happens when the shorter-term moving average falls below the longer-term moving average, indicating a possible downtrend. Traders often use these crossover signals to initiate trades or confirm existing positions.
4. Trend Reversals:
Moving averages can also help in identifying potential trend reversals in the market. When a moving average that was acting as a support or resistance level is breached decisively, it could signal a shift in the prevailing trend. For instance, if a price that was above a rising moving average suddenly breaks below it, it could indicate a trend reversal from bullish to bearish. By monitoring the interaction between price and moving averages, traders can stay ahead of trend changes and adjust their positions accordingly.
5. Entry and Exit Points:
Finally, moving averages can assist traders in determining optimal entry and exit points for their trades. During a strong uptrend, traders may wait for a pullback towards a key moving average, such as the 20-day or 50-day moving average, to enter a long position at a favorable price. Conversely, in a downtrend, traders might look to short the market when the price rallies towards a declining moving average. By combining moving averages with other technical indicators and price action analysis, traders can improve their timing and increase the probability of successful trades.
In conclusion, moving averages are versatile tools that offer a wide range of applications in technical analysis. From trend identification to entry and exit signals, moving averages can enhance a trader’s decision-making process and improve trading outcomes. By mastering the various uses of moving averages and incorporating them into a comprehensive trading strategy, traders can gain a competitive edge in the dynamic and fast-paced financial markets.