In a dynamic economic landscape undergoing rapid technological advancements, the labor market in the United States is witnessing a significant shift towards skilled labor positions, while the hiring for traditional white-collar jobs has been slowing down. This transition reflects the evolving needs of industries and the changing nature of work in the digital age.
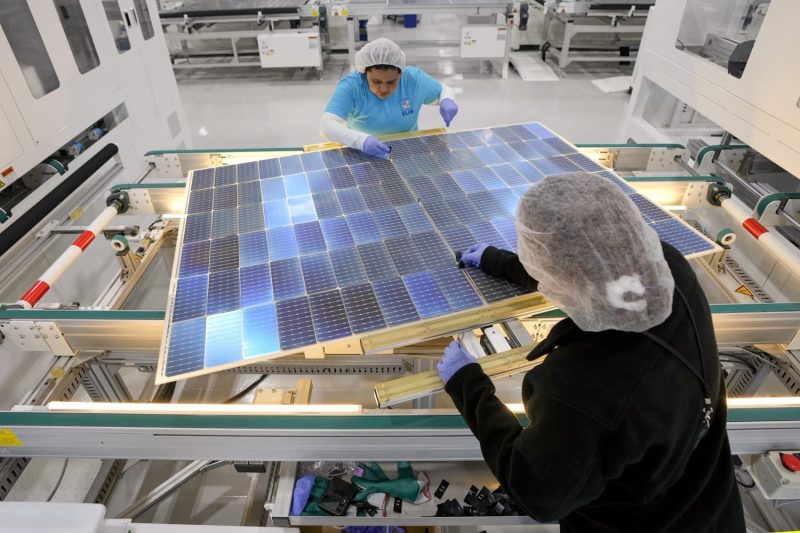
The increasing demand for skilled labor can be attributed to various factors, including the growing emphasis on specialized technical skills required in modern workplaces. With industries such as IT, healthcare, engineering, and manufacturing experiencing continual innovation and automation, there is a higher demand for workers who possess advanced technical competencies and expertise in specialized fields.
Moreover, the rise of the gig economy and remote work arrangements has also contributed to the shift towards skilled labor. Organizations are increasingly relying on freelancers, contractors, and remote workers to fulfill specific roles and projects, creating opportunities for individuals with specialized skills to thrive in non-traditional work settings.
As the nature of work evolves, there is a greater focus on lifelong learning and upskilling among workers to remain competitive in the job market. Continuous learning and professional development have become essential for individuals seeking to adapt to the changing demands of their industries and secure employment in increasingly competitive sectors.
However, the shift towards skilled labor also presents challenges, particularly for individuals who may lack access to quality education and training programs needed to acquire the necessary skills for in-demand jobs. Addressing this disparity requires a concerted effort from policymakers, educators, and employers to create pathways for upskilling and reskilling opportunities for workers from diverse backgrounds.
Additionally, the growing importance of skilled labor underscores the need for collaboration between educational institutions, industry stakeholders, and policymakers to align training programs with the evolving demands of the labor market. By fostering strategic partnerships and investing in workforce development initiatives, stakeholders can ensure that individuals are equipped with the skills needed to succeed in the rapidly changing economy.
In conclusion, the shift towards skilled labor in the U.S. labor market reflects the changing dynamics of work in the digital age, driven by technological advancements, the gig economy, and the need for specialized technical skills. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for workers with advanced skills and expertise is expected to grow, highlighting the importance of lifelong learning, upskilling, and collaboration among stakeholders to address the needs of a rapidly changing labor market.