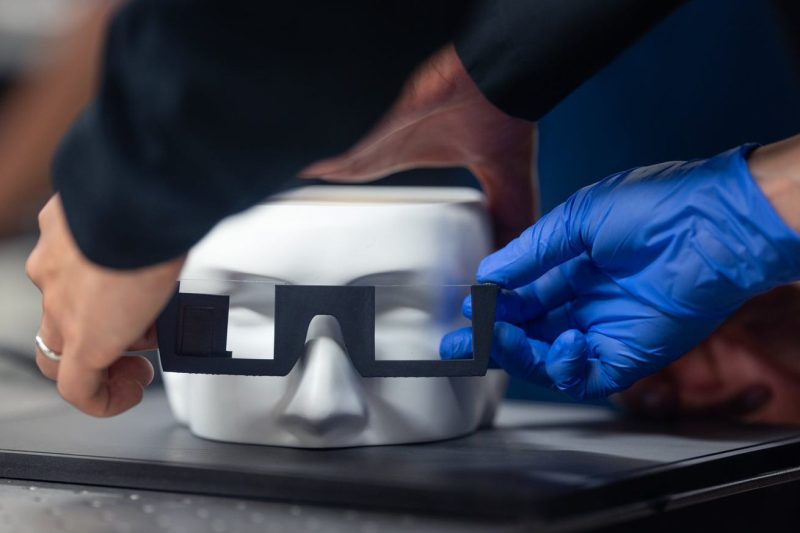
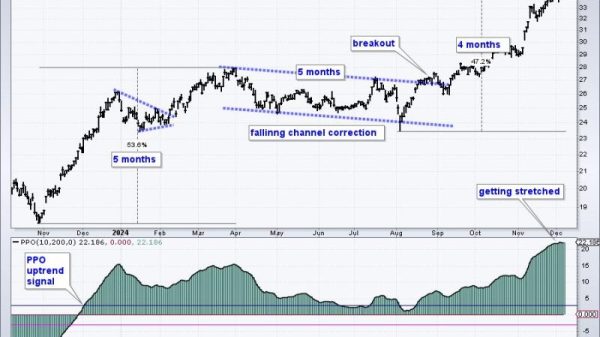
Stanford University researchers have recently unveiled a pioneering prototype that could potentially redefine the future of augmented reality (AR) glasses. The innovative design, showcased in a recent online presentation, showcases cutting-edge technology that could revolutionize how we interact with digital information in the physical world.
The Stanford team’s prototype stands out for its sleek and minimalist design, which aims to address one of the longstanding challenges of AR glasses – bulkiness. By incorporating advanced optics and display technologies, the prototype achieves a high level of transparency, enabling users to seamlessly overlay digital content onto their real-world surroundings. This breakthrough in design not only enhances user comfort but also contributes to a more immersive AR experience.
One of the key features of the Stanford prototype is its integration of advanced gesture recognition technology. By leveraging sophisticated sensors and algorithms, the AR glasses can accurately track hand movements and gestures, allowing users to interact with digital interfaces in a more intuitive and natural manner. This hands-free interaction opens up a wide range of possibilities for applications in various fields, from gaming and entertainment to education and professional training.
Moreover, the prototype boasts impressive spatial mapping capabilities, enabling it to create detailed and dynamic 3D maps of the user’s environment in real time. This feature enhances the accuracy and precision of AR content placement, ensuring that digital overlays align seamlessly with physical objects and surfaces. The result is a more realistic and engaging AR experience that blurs the boundaries between the digital and physical worlds.
Another notable aspect of the Stanford prototype is its robust connectivity options, which allow seamless integration with a variety of devices and platforms. By supporting standard wireless protocols and APIs, the AR glasses can interact with smartphones, tablets, and other smart devices, enabling users to access and control a wide range of digital content and services.
In conclusion, the Stanford University prototype represents a significant step forward in the evolution of AR glasses, showcasing the potential for a more immersive, intuitive, and seamlessly integrated AR experience. By pushing the boundaries of design and technology, the researchers have laid the groundwork for future innovations that could transform how we interact with and perceive the world around us. As the technology continues to advance, we can expect AR glasses to become more sophisticated, versatile, and ubiquitous, unlocking new possibilities across various industries and applications.