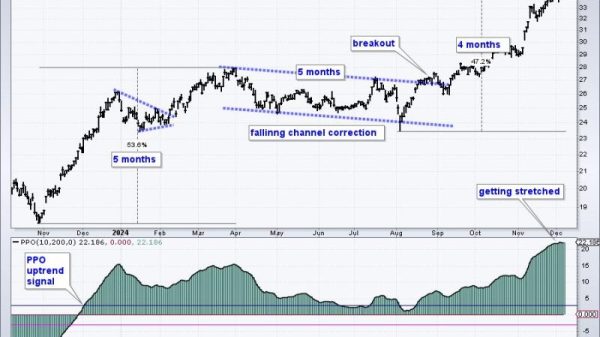
The article dives into the potential consequences of a negative divergence affecting Google’s stock price. A negative divergence occurs when the price of a financial asset is moving in the opposite direction to a technical indicator, suggesting a potential reversal in the stock’s momentum.
In the case of Google, the negative divergence could have several outcomes. Firstly, it could lead to a decline in the stock price as investors react to the signal of weakening momentum. This could result in a short-term selling pressure as speculators and traders adjust their positions based on the divergence.
Moreover, such a divergence might also prompt institutional investors to reevaluate their holdings in Google. Large investors like mutual funds and pension funds rely on technical indicators to make decisions, and a negative divergence could trigger a reassessment of Google’s prospects.
Additionally, a negative divergence in Google’s stock price could impact market sentiment towards the tech sector as a whole. Google, being a leading player in the tech industry, often sets the tone for the broader market. A significant downturn in its stock price could spook investors and lead to a broader sell-off in tech stocks.
Furthermore, the negative divergence could also result in increased volatility in Google’s stock. Investors tend to react strongly to technical signals, and a divergence of this nature could lead to heightened trading activity and price fluctuations.
In conclusion, a negative divergence in Google’s stock price could have far-reaching implications for the company, its investors, and the broader tech sector. It could lead to a decline in the stock price, prompt institutional investors to reassess their positions, impact market sentiment, and increase volatility in the stock. Investors and stakeholders will need to closely monitor the situation and adapt their strategies accordingly to navigate any potential fallout from the execution of this negative divergence.